Non-gynaecological Cytology
Head and neck cytology
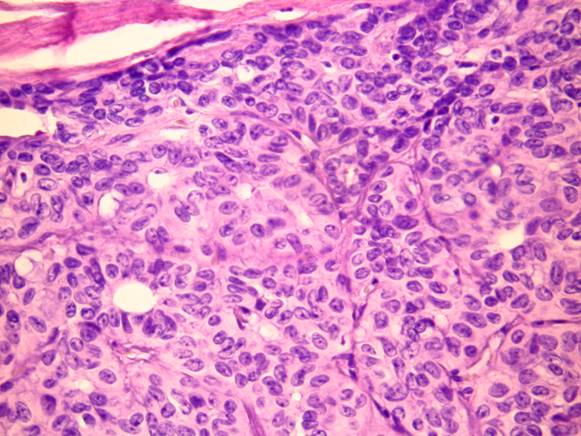
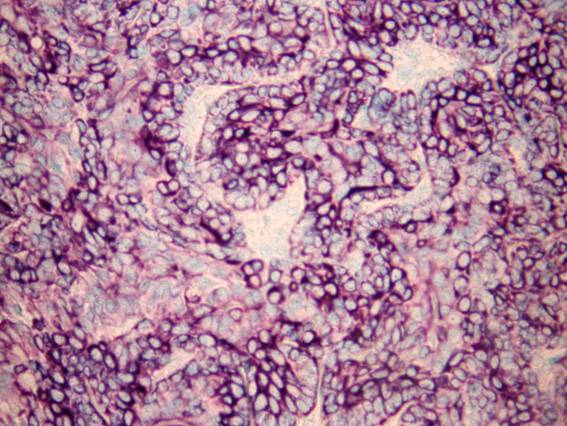
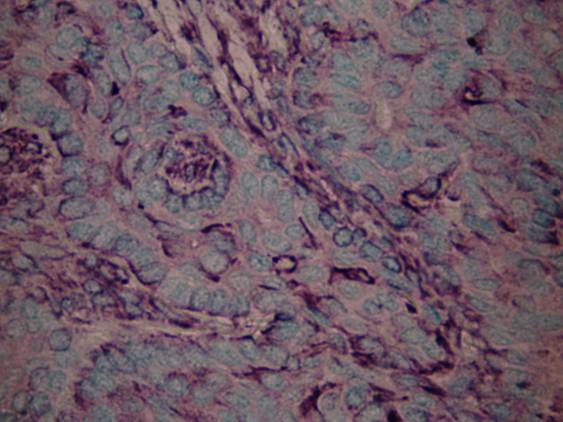
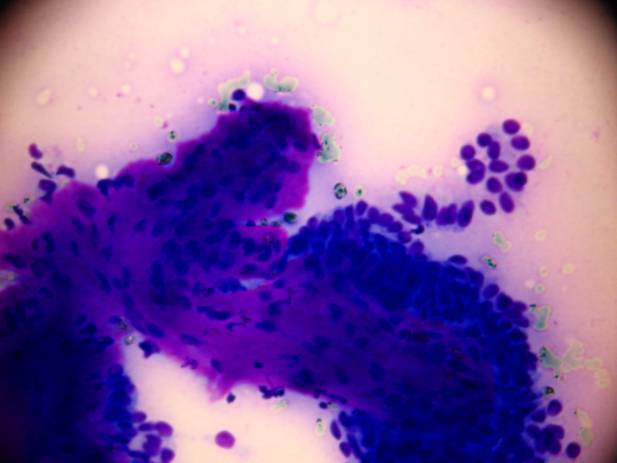
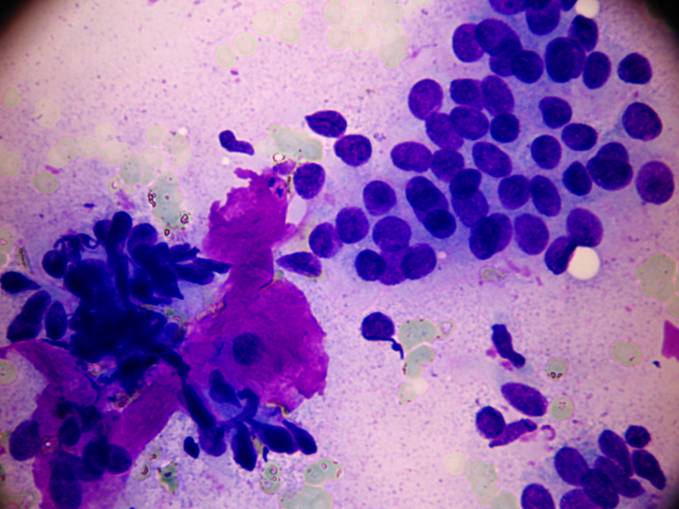
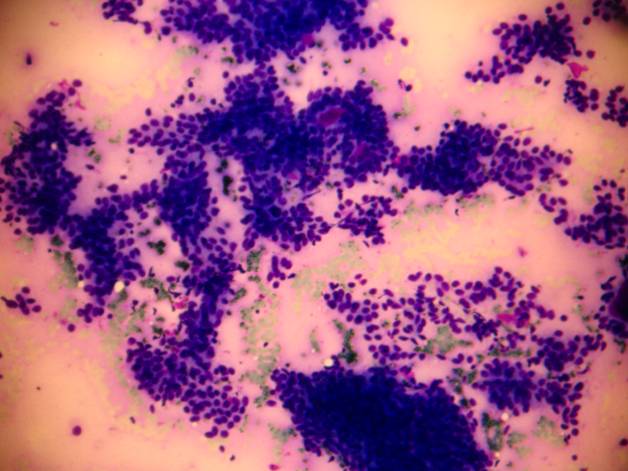
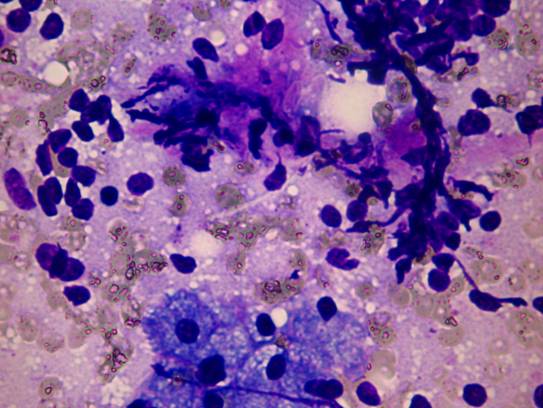
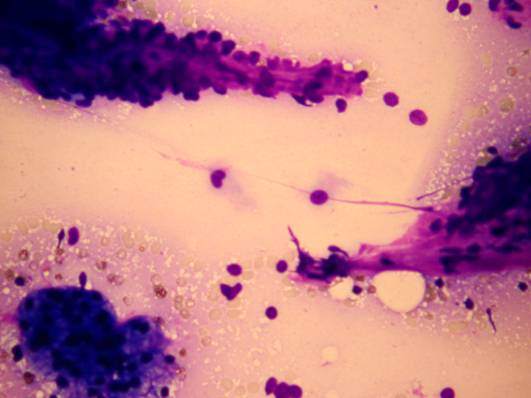
Epithelial / myoepithelial carcinoma
The tumor is composed of two cell types which form duct-like structures: ductal cells (inner layer), clear myoepithelial cells (outer layer). They can be distinguished by immunocytochemistry: the former are pan-keratin positive, the latter are S-100 positive. The cytology is that of a malignant clear cell tumor, with varying degrees of cellular and nuclear atypia. There are both tissue fragments and isolated cells; the cells may be arranged in solid and papillary structures. The stromal component is metachromatic, with a hyaline, elongated appearance. In some occasions duct-like or globular structures are also found. The cytologic pattern suggests a malignant growth.
Epithelial / myoepithelial carcinoma - PAN CK Epithelial / myoepithelial carcinoma - S-100